Quicksort is a divide and conquer algorithm. The steps are: 1) Pick an element from the array, this element is called as pivot element. 2) Divide the unsorted array of elements in two arrays with values less than the pivot come in the first sub array, while all elements with values greater than the pivot come in the second sub-array (equal values can go either way). This step is called the partition operation. 3) Recursively repeat the step 2(until the sub-arrays are sorted) to the sub-array of elements with smaller values and separately to the sub-array of elements with greater values. The same logic we have implemented in the following C program.
C Program – Quicksort algorithm implementation
#include<stdio.h>
void quicksort(int number[25],int first,int last){
int i, j, pivot, temp;
if(first<last){
pivot=first;
i=first;
j=last;
while(i<j){
while(number[i]<=number[pivot]&&i<last)
i++;
while(number[j]>number[pivot])
j--;
if(i<j){
temp=number[i];
number[i]=number[j];
number[j]=temp;
}
}
temp=number[pivot];
number[pivot]=number[j];
number[j]=temp;
quicksort(number,first,j-1);
quicksort(number,j+1,last);
}
}
int main(){
int i, count, number[25];
printf("How many elements are u going to enter?: ");
scanf("%d",&count);
printf("Enter %d elements: ", count);
for(i=0;i<count;i++)
scanf("%d",&number[i]);
quicksort(number,0,count-1);
printf("Order of Sorted elements: ");
for(i=0;i<count;i++)
printf(" %d",number[i]);
return 0;
}
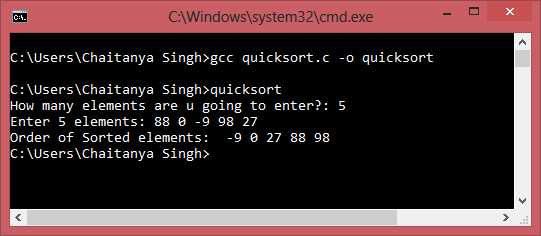
Output:



Comments
Post a Comment